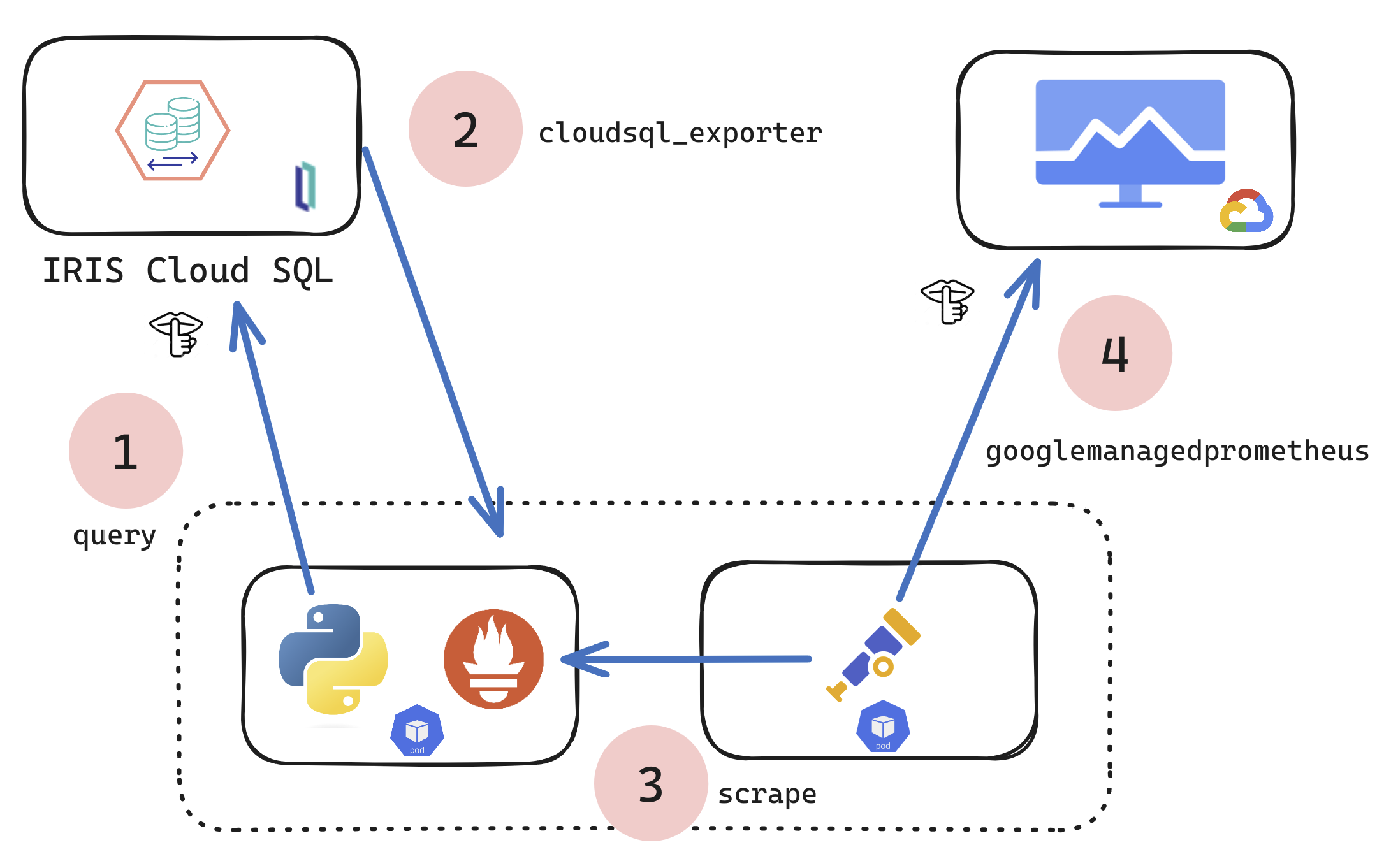
If you are a customer of the new InterSystems IRIS® Cloud SQL and InterSystems IRIS® Cloud IntegratedML® cloud offerings and want access to the metrics of your deployments and send them to your own Observability platform, here is a quick and dirty way to get it done by sending the metrics to Google Cloud Platform Monitoring (formerly StackDriver).
The Cloud portal does contain a representation of some top level metrics for at-a-glance heads up metrics, which is powered by a metrics endpoint that is exposed to you, but without some inspection you would not know it was there.
🚩 This approach is most likely taking advantage of a "to be named feature", so with that being said, it is not future-proof and definitely not supported by InterSystems.
So what if you wanted a more comprehensive set exported? This technical article/example shows a technique to scrape and forward metrics to observability, it can be modified to suit your needs, to scrape ANY metrics target and send to ANY observability platform using the Open Telemetry Collector.
The mechanics leading up to the above result can be accomplished in many ways, but for here we are standing up a Kubernetes pod to run a python script in one container, and Otel in another to pull and push the metrics... definitely a choose your own adventure, but for this example and article k8s is the actor pulling this off with Python.
Steps:
- Prereqs
- Python
- Container
- Kubernetes
- Google Cloud Monitoring
Prerequisites:
- An active subscription to IRIS® Cloud SQL
- One Deployment, running, optionally with Integrated ML
- Secrets to supply to your environment
Environment Variables
I dropped this in a teaser as it is a bit involved and somewhat off target of the point, but these are the values you will need to generate the secrets.
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USER 'user'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_PASS 'pass'
☝ These are your credentials for https://portal.live.isccloud.io
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USERPOOLID 'userpoolid'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_CLIENTID 'clientid'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_API 'api'
☝ These you have to dig out of development tools for your browser.
- `aud` = clientid
- `userpoolid`= iss
- `api` = request utl
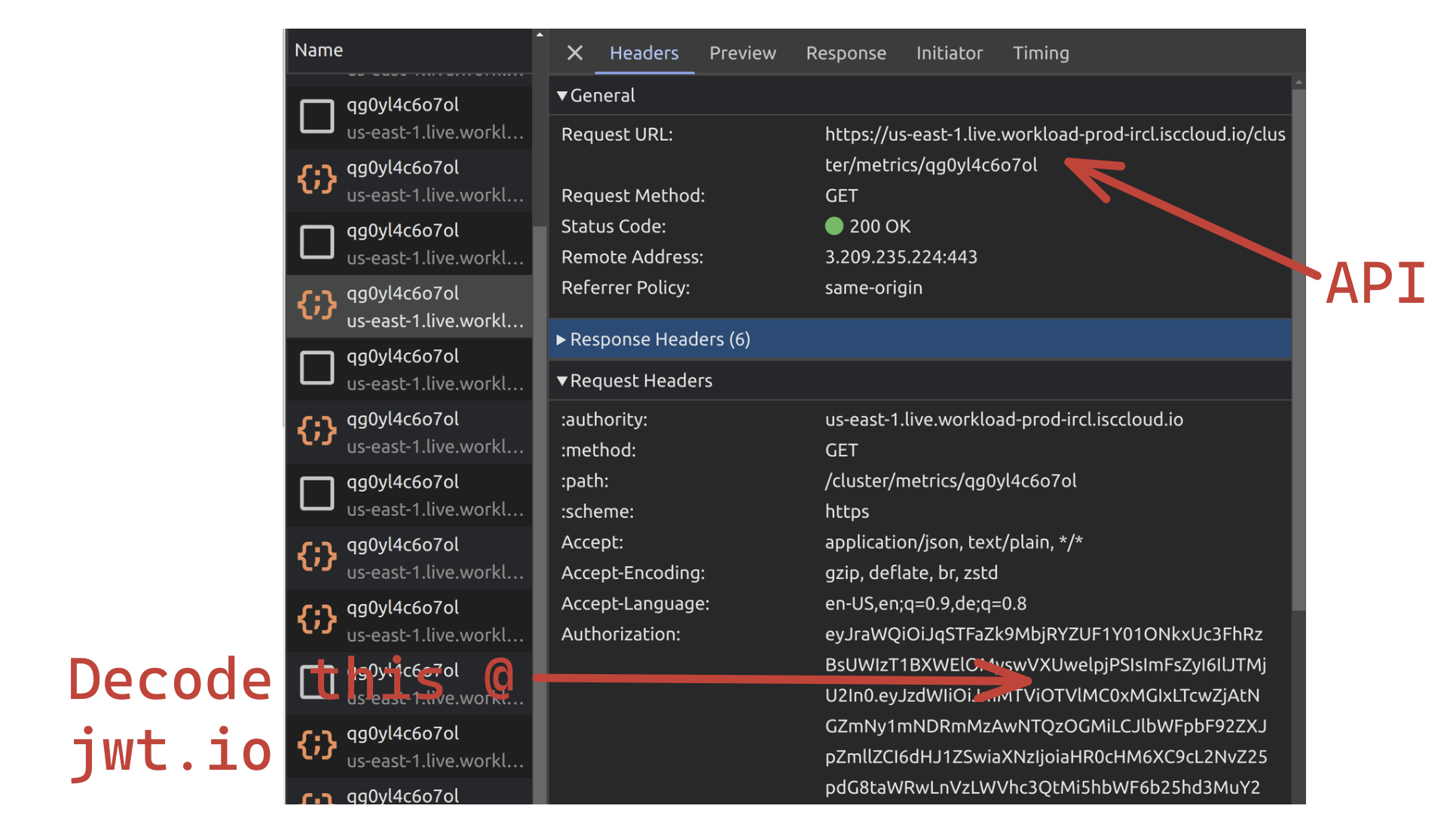
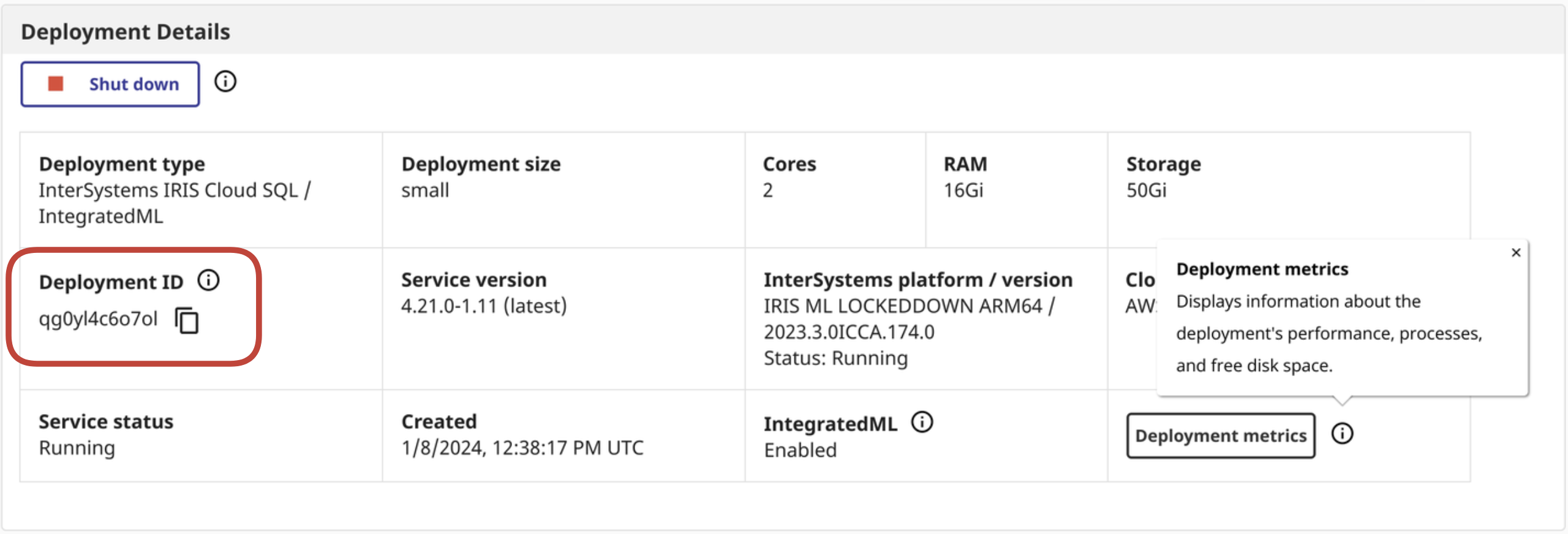
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_DEPLOYMENTID 'deploymentid'
☝ This can be derived from the Cloud Service Portal
Python:
Here is the python hackery to pull the metrics from the Cloud Portal and export them locally as metrics for the otel collector to scrape:
iris_cloudsql_exporter.py
import time
import os
import requests
import json
from warrant import Cognito
from prometheus_client.core import GaugeMetricFamily, REGISTRY, CounterMetricFamily
from prometheus_client import start_http_server
from prometheus_client.parser import text_string_to_metric_families
class IRISCloudSQLExporter(object):
def __init__(self):
self.access_token = self.get_access_token()
self.portal_api = os.environ['IRIS_CLOUDSQL_API']
self.portal_deploymentid = os.environ['IRIS_CLOUDSQL_DEPLOYMENTID']
def collect(self):
url = self.portal_api
deploymentid = self.portal_deploymentid
print(url)
print(deploymentid)
headers = {
'Authorization': self.access_token,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
metrics_response = requests.request("GET", url + '/metrics/' + deploymentid, headers=headers)
metrics = metrics_response.content.decode("utf-8")
for iris_metrics in text_string_to_metric_families(metrics):
for sample in iris_metrics.samples:
labels_string = "{1}".format(*sample).replace('\'',"\"")
labels_dict = json.loads(labels_string)
labels = []
for d in labels_dict:
labels.extend(labels_dict)
if len(labels) > 0:
g = GaugeMetricFamily("{0}".format(*sample), 'Help text', labels=labels)
g.add_metric(list(labels_dict.values()), "{2}".format(*sample))
else:
g = GaugeMetricFamily("{0}".format(*sample), 'Help text', labels=labels)
g.add_metric([""], "{2}".format(*sample))
yield g
def get_access_token(self):
try:
user_pool_id = os.environ['IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USERPOOLID']
username = os.environ['IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USER']
password = os.environ['IRIS_CLOUDSQL_PASS']
clientid = os.environ['IRIS_CLOUDSQL_CLIENTID']
print(user_pool_id)
print(username)
print(password)
print(clientid)
try:
u = Cognito(
user_pool_id=user_pool_id,
client_id=clientid,
user_pool_region="us-east-2",
username=username
)
u.authenticate(password=password)
except Exception as p:
print(p)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return u.id_token
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_http_server(8000)
REGISTRY.register(IRISCloudSQLExporter())
while True:
REGISTRY.collect()
print("Polling IRIS CloudSQL API for metrics data....")
time.sleep(120)
Docker:
FROM python:3.8
ADD src /src
RUN pip install prometheus_client
RUN pip install requests
WORKDIR /src
ENV PYTHONPATH '/src/'
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USERPOOLID 'userpoolid'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_CLIENTID 'clientid'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USER 'user'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_PASS 'pass'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_API 'api'
ENV IRIS_CLOUDSQL_DEPLOYMENTID 'deploymentid'
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
CMD ["python" , "/src/iris_cloudsql_exporter.py"]
docker build -t iris-cloudsql-exporter .
docker image tag iris-cloudsql-exporter sween/iris-cloudsql-exporter:latest
docker push sween/iris-cloudsql-exporter:latest
Deployment:
k8s; Create us a namespace:
kubectl create ns iris
k8s; Add the secret:
kubectl create secret generic iris-cloudsql -n iris \
--from-literal=user=$IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USER \
--from-literal=pass=$IRIS_CLOUDSQL_PASS \
--from-literal=clientid=$IRIS_CLOUDSQL_CLIENTID \
--from-literal=api=$IRIS_CLOUDSQL_API \
--from-literal=deploymentid=$IRIS_CLOUDSQL_DEPLOYMENTID \
--from-literal=userpoolid=$IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USERPOOLID
otel, Create Config:
apiVersion: v1
data:
config.yaml: |
receivers:
prometheus:
config:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'IRIS CloudSQL'
# Override the global default and scrape targets from this job every 5 seconds.
scrape_interval: 30s
scrape_timeout: 30s
static_configs:
- targets: ['192.168.1.96:5000']
metrics_path: /
exporters:
googlemanagedprometheus:
project: "pidtoo-fhir"
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [prometheus]
exporters: [googlemanagedprometheus]
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: otel-config
namespace: iris
k8s; Load the otel config as a configmap:
kubectl -n iris create configmap otel-config --from-file config.yaml
k8s; deploy load balancer (definitely optional), MetalLB. I do this to scrape and inspect from outside of the cluster.
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -n iris -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: iris-cloudsql-exporter-service
spec:
selector:
app: iris-cloudsql-exporter
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 5000
targetPort: 8000
EOF
gcp; need the keys to google cloud, the service account needs to be scoped
roles/monitoring.metricWriter
kubectl -n iris create secret generic gmp-test-sa --from-file=key.json=key.json
k8s; the deployment/pod itself, two containers:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: iris-cloudsql-exporter
labels:
app: iris-cloudsql-exporter
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: iris-cloudsql-exporter
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: iris-cloudsql-exporter
spec:
containers:
- name: iris-cloudsql-exporter
image: sween/iris-cloudsql-exporter:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
env:
- name: "GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS"
value: "/gmp/key.json"
- name: IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USERPOOLID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: iris-cloudsql
key: userpoolid
- name: IRIS_CLOUDSQL_CLIENTID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: iris-cloudsql
key: clientid
- name: IRIS_CLOUDSQL_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: iris-cloudsql
key: user
- name: IRIS_CLOUDSQL_PASS
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: iris-cloudsql
key: pass
- name: IRIS_CLOUDSQL_API
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: iris-cloudsql
key: api
- name: IRIS_CLOUDSQL_DEPLOYMENTID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: iris-cloudsql
key: deploymentid
- name: otel-collector
image: otel/opentelemetry-collector-contrib:0.92.0
args:
- --config
- /etc/otel/config.yaml
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/otel/
name: otel-config
- name: gmp-sa
mountPath: /gmp
readOnly: true
env:
- name: "GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS"
value: "/gmp/key.json"
volumes:
- name: gmp-sa
secret:
secretName: gmp-test-sa
- name: otel-config
configMap:
name: otel-config
kubectl -n iris apply -f deployment.yaml
Running
Assuming nothing is amiss, lets peruse the namespace and see how we are doing.
✔ 2 config maps, one for GCP, one for otel
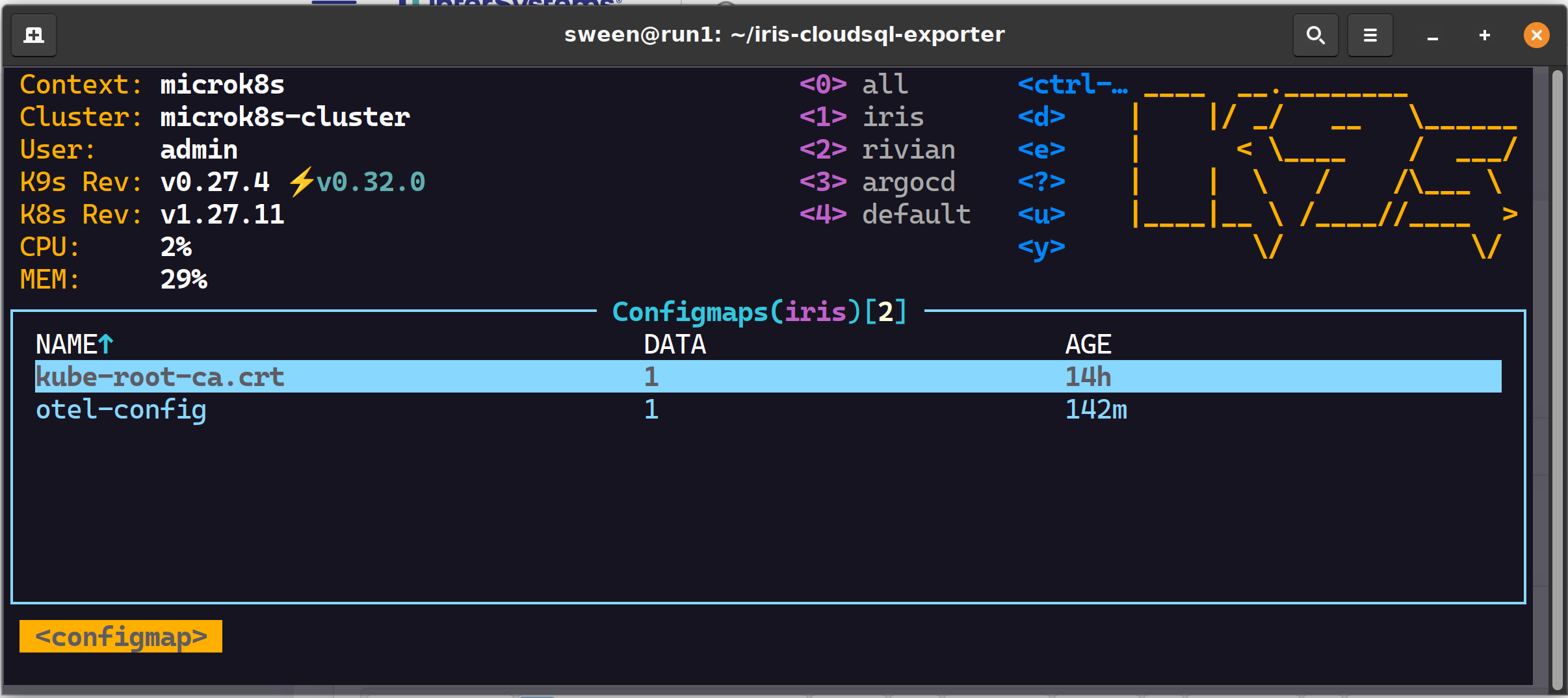
✔ 1 load balancer
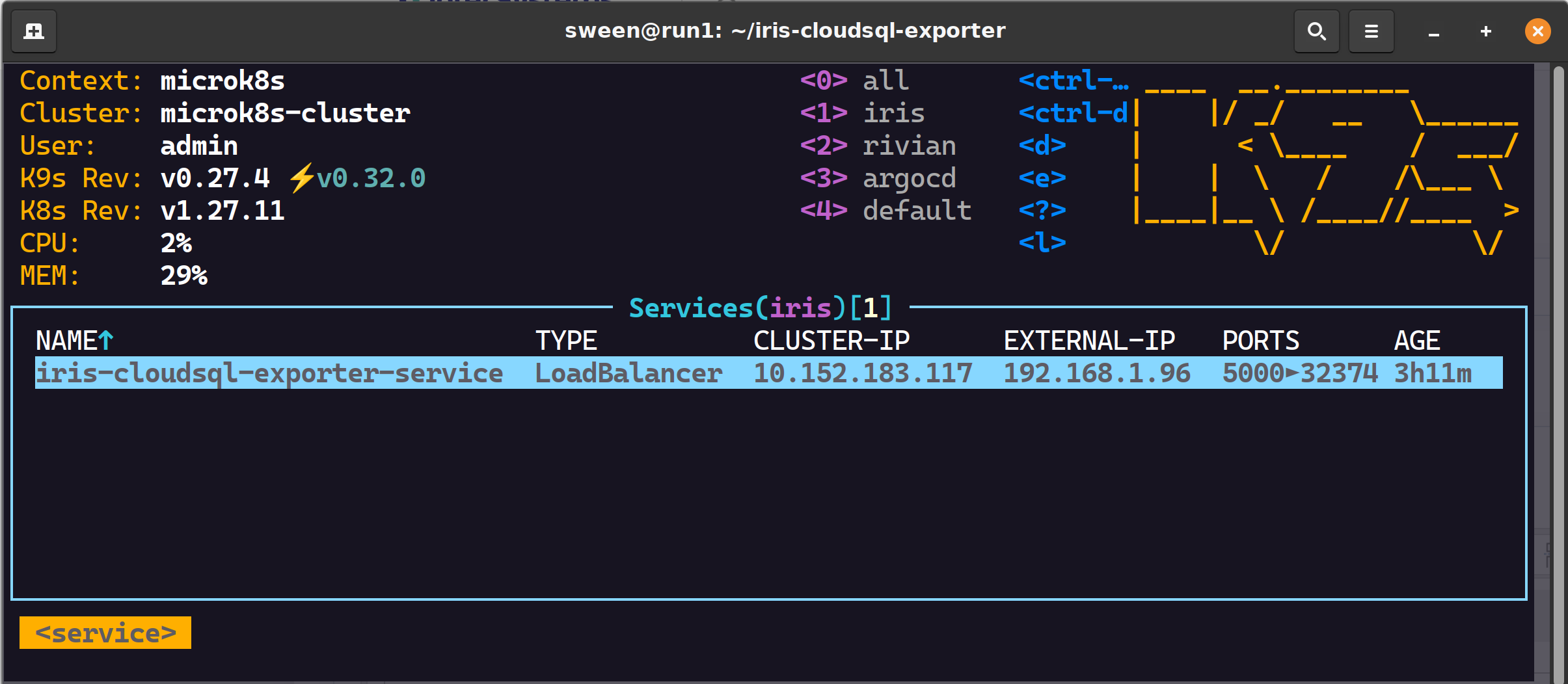
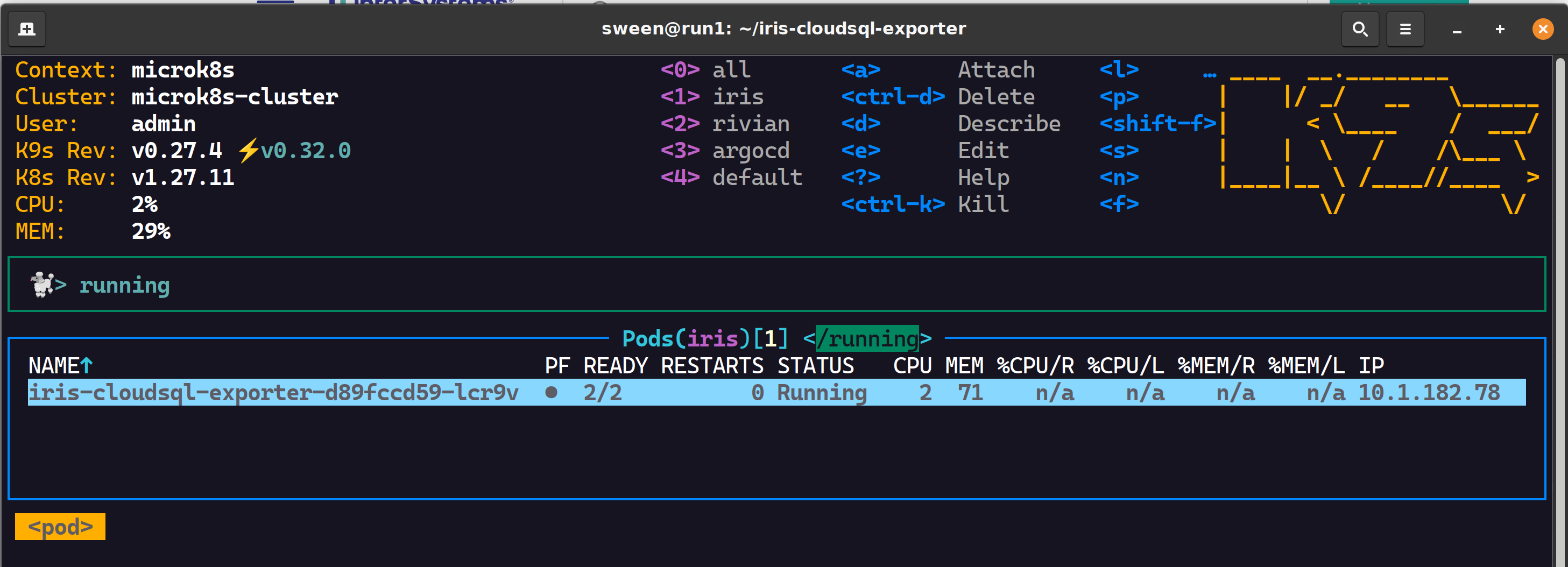
✔ 1 pod, 2 containers successful scrapes
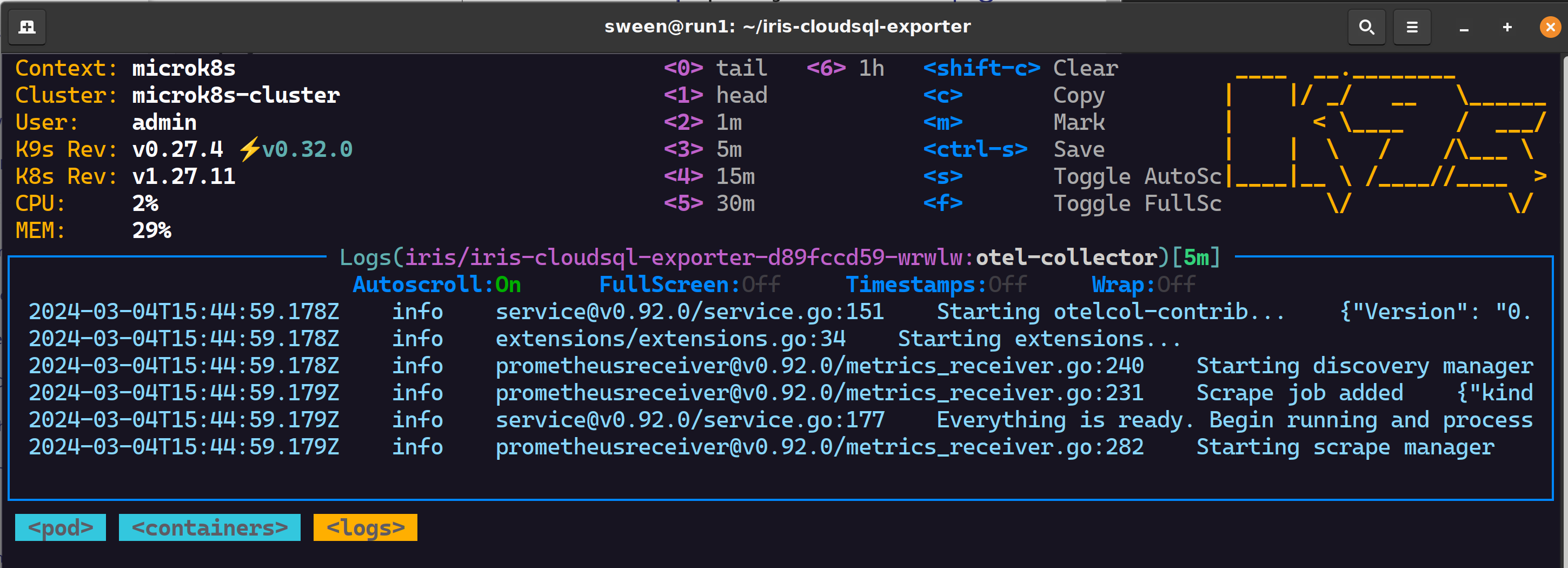
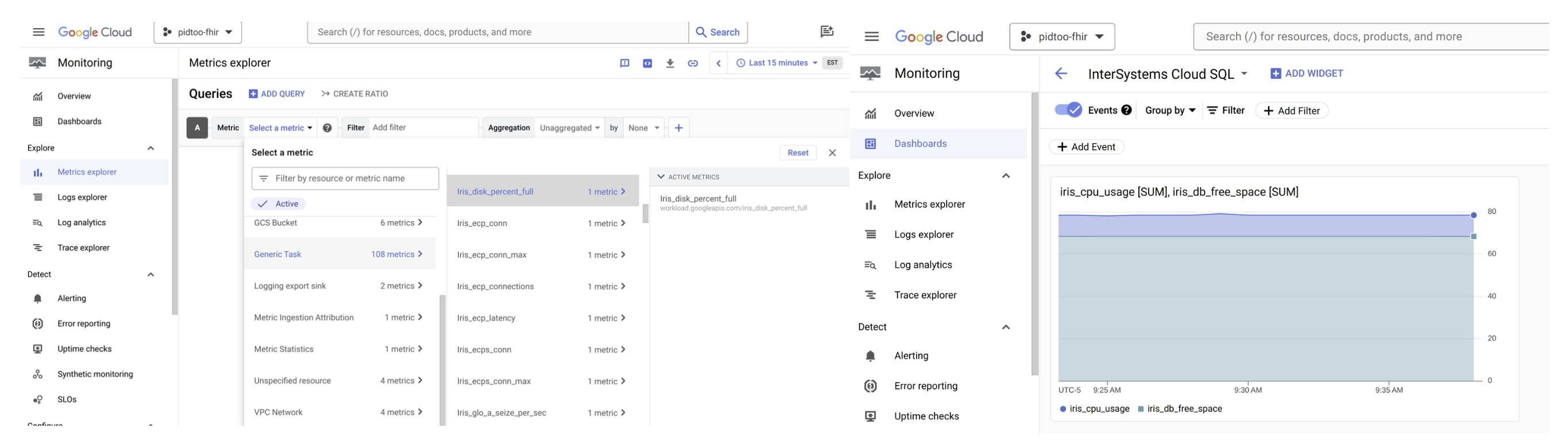
Google Cloud Monitoring
Inspect observability to see if the metrics are arriving ok and be awesome in observability!

.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)







